[备份] Java并发之LongAdder源码浅析
介绍
高并发下做数据统计,如果采用AtomicLong的方式会存在问题
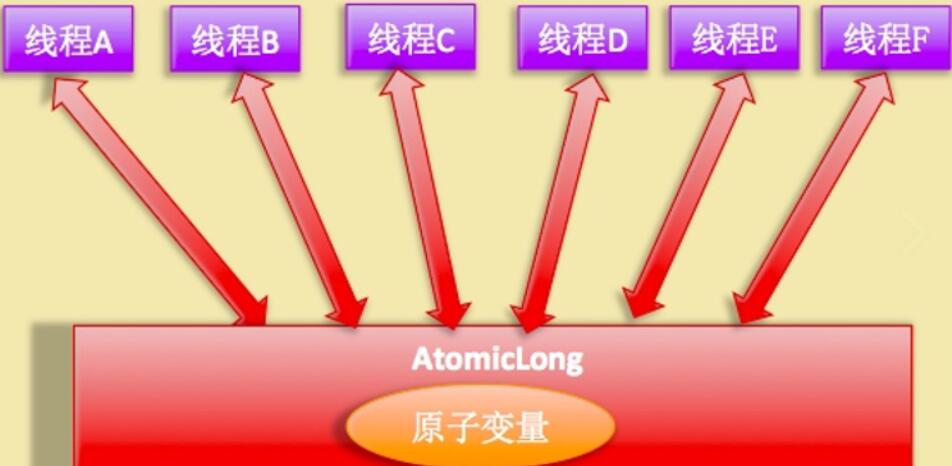
AtomicLong.getAndIncrement方法使用到unsafe类
xxxxxxxxxxpublic final long getAndIncrement() { return unsafe.getAndAddLong(this, valueOffset, 1L);}跟入unsafe类看到底层实现是CAS。高并发情况下,多个线程同时卡在循环中,效率过低。另外CAS有ABA问题(原理和解决参考上一篇文章)
xxxxxxxxxxpublic final long getAndAddLong(Object var1, long var2, long var4) { long var6; do { var6 = this.getLongVolatile(var1, var2); } while(!this.compareAndSwapLong(var1, var2, var6, var6 + var4));
return var6;}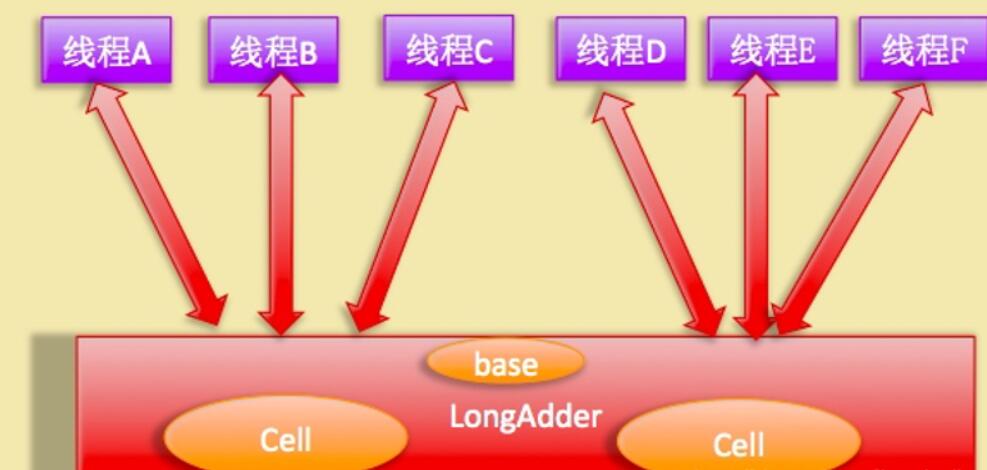
于是出现了一个新的类:LongAddr
源码
Striped64
首先来看Cell数组中的Cell是什么
xxxxxxxxxx.misc.Contended static final class Cell { // cell中的value volatile long value; Cell(long x) { value = x; } // CAS操作 final boolean cas(long cmp, long val) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, cmp, val); }
// Unsafe mechanics private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; // value的内存偏移 private static final long valueOffset; static { try { // 反射构造unsafe UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class<?> ak = Cell.class; valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (ak.getDeclaredField("value")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new Error(e); } }}Cell数组长度条件取决于CPU数量,后续分析
xxxxxxxxxxstatic final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();没有发生竞争或cells扩容时,需要写入base
xxxxxxxxxxtransient volatile long base;
// CAS操作basefinal boolean casBase(long cmp, long val) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASE, cmp, val);}初始化cells或扩容都需要锁,0表示无锁,1表示其他线程持有锁
xxxxxxxxxxtransient volatile int cellsBusy;
// CAS上锁final boolean casCellsBusy() { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1);}当前线程的哈希值
xxxxxxxxxx// 获取static final int getProbe() { return UNSAFE.getInt(Thread.currentThread(), PROBE);}
// 重置static final int advanceProbe(int probe) { probe ^= probe << 13; // xorshift probe ^= probe >>> 17; probe ^= probe << 5; UNSAFE.putInt(Thread.currentThread(), PROBE, probe); return probe;}
add
从LongAdder的add方法进入
xxxxxxxxxxpublic void add(long x) { // cells引用 Cell[] as; // base值和期望值 long b, v; // cells数组长度 int m; // 当前线程命中的cell Cell a; // cells已被初始化,当前线程应该将数据写入对于的cell中 // cells如果没有被初始化,应该将数据写入base中 // casBase为true表示当前线程cas替换数据成功(注意有取反) // casBase为false表示发生了竞争,需要重试或扩容(注意有取反) if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) { // cells已被初始化或需要重试或扩容时会进入 // true:未竞争 false:有竞争 boolean uncontended = true; // 条件1:as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 // true表示cells未被初始化,说明发生了竞争 // false表示cells已被初始化,说明没有发生竞争 // 条件2:简单理解为获取当前线程hash值,由于length是2次方数,m二进制各位都是1,一定小于长度 // ture表示当前线程对应下标cell为空,需要创建longAccumulate支持 // false说明当前线程对应cell不为空,下一步要将x值添加到cell中 // 条件3:true表示cas操作失败,说明当前线程对应cell有竞争(注意有取反) // false吧cas成功(注意有取反) if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 || (a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null || !(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x))) // 重试、扩容、初始化cells longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended); }}
longAccumulate
这是LongAdder的核心方法,进入该方法的三大条件:
- cells未被初始化,说明发生了竞争,需要初始化
- 当前线程对应下标cell为空,需要创建longAccumulate支持
- cas操作失败,说明当前线程对应cell有竞争,需要重试或扩容
xxxxxxxxxxfinal void longAccumulate(long x, LongBinaryOperator fn, boolean wasUncontended) { // 线程的哈希值 int h; // 哈希值初始化 if ((h = getProbe()) == 0) { ThreadLocalRandom.current(); h = getProbe(); // 默认情况当前线程写入cell[0]发生竞争 // 但不认为这是真正的竞争 wasUncontended = true; } // 扩容意向:true一定会扩容 boolean collide = false; for (;;) { // cells引用 Cell[] as; // 当前线程命中的cell Cell a; // cells数组长度 int n; // 期望值 long v; // cells已经初始化,当前线程应该将数据写入对应cell中 if ((as = cells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) { // 寻址算法得到的cell为空,需要创建 if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) { // 锁是否被占用 if (cellsBusy == 0) { // 创建cell,设置value为x Cell r = new Cell(x); // 当前无锁,可以竞争,上锁 if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) { // 是否创建成功 boolean created = false; try { // 当前cells引用 Cell[] rs; // m是cells长度,j是当前线程命中cells下标 int m, j; // 条件1和条件2是验证,没意义 // 条件3:寻址拿到的cell位置是空 // 避免其他线程已经处理过 if ((rs = cells) != null && (m = rs.length) > 0 && rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) { // 设置cells对应下标 rs[j] = r; // 创建成功 created = true; } } finally { // 释放锁 cellsBusy = 0; } if (created) // 创建成功break break; continue; } } // 锁被占用不扩容 collide = false; } // cells初始化之后,并且当前线程竞争修改失败 else if (!wasUncontended) wasUncontended = true; // 重置过的hash值,新命中的cell不为空 // 如果写成功后退出,如果失败说明新的哈希值再次竞争 else if (a.cas(v = a.value, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) break; // 数组长度大于CPU数,或其他线程已经扩容过 else if (n >= NCPU || cells != as) // 不再扩容 collide = false; else if (!collide) // 设置扩容意向为true但不 collide = true; // 扩容逻辑 // 当前无锁,可以竞争,上锁 else if (cellsBusy == 0 && casCellsBusy()) { try { // double check if (cells == as) { // 左移长度翻倍 Cell[] rs = new Cell[n << 1]; // 拷贝 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) rs[i] = as[i]; // 赋值 cells = rs; } } finally { // 释放锁 cellsBusy = 0; } // 不用再扩容 collide = false; continue; } // 重置当前线程哈希值 h = advanceProbe(h); } // cells数据还未初始化 // 未加锁 // 其他线程没有修改cells // 获取锁成功(cellsBusy改为1) else if (cellsBusy == 0 && cells == as && casCellsBusy()) { boolean init = false; try { // 再次确认其他线程在拿锁时候没有修改cells if (cells == as) { // 初始化 Cell[] rs = new Cell[2]; rs[h & 1] = new Cell(x); cells = rs; init = true; } } finally { // 释放锁 cellsBusy = 0; } if (init) break; } // 其他线程正在初始化cells,拿锁失败,当前线程累加base // cells已经被初始化,当前线程需要将数据累加到base else if (casBase(v = base, ((fn == null) ? v + x : fn.applyAsLong(v, x)))) break; }}
sum
获取的方法就很简单了,base加cell数组的value
xxxxxxxxxxpublic long sum() { Cell[] as = cells; Cell a; long sum = base; if (as != null) { for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) { if ((a = as[i]) != null) sum += a.value; } } return sum;}